Chapter 1
BIOLOGY AND ITS MAUOR FIELDS OF SPECIALIZATION
Q.No 1:
Define the term biology.
Answer:
BIOLOGY:
The word biology has been derived from two Greek words, bios and logos . Bio means life and logos means science, discussion, thinking, discourse or reasoning So, biology is the study of living things.
The word life itself has been derived from Latin word Laben which mean soul.
Q.No 2
Define life. What are the living things?
Answer:
LIFE:
For biologists, life is a set of characteristics that distinguish living organisms from non-living objects (including dead organisms).
LIVING THINGS:
Living organisms are highly organized, complex entities; are composed of one or more cells, contain genetic program of their characteristics; can acquire and use energy, can cary out and control numerous chemical reactions, can grow in size, maintain a fairly constant internal environment, produce offspring similar to themselves; respond to changes in their environment. Any object possessing all these characteristics simultaneously can be declared as living thing.
Q.No 3
What are the main branches of biology?
Answer:
There are two main disciplines of biology. Botany == Study of plants
Zoology = Study of animals.
There are also a number of other branches of biology such as: Molecular Biology, Microbiology, Marine Biology, Environmental Biology, Fresh water Biology, Parasitology, Human Biology, Social Biology Biotechnology, etc,
Molecular Biology:
Molecular biology is a branch of biology which deals with the structure organisms, their cells and their organelles at molecular level.
Microbiology:
This is the study of microorganisms, which include Bacteria, Viruses, Protozoa and microscopic algae and fungi .
Fresh Water Biology:
This branch of biology deals with the organisms living in freshwater bodies ie rivers, lakes etc and physical and chemical parameters of the water bodies.
Marine Biology:
This is the study of life in seas and oceans. This includes the study of the marine life and the physical and chemical characteristics of the sea acting as factors for marine life.
Parasitology:
This is the branch of biology, which deals with the study of parasites. The structure, mode of transmission, life histories and host parasite relationships are studied in parasitology.
Human Biology:
It deals with the study of man. This includes structure, function, histology anatomy, morphology, evolution, genetics, cell biology and ecological studies of human beings.
Social Biology:
This is the branch of biology, which deals with the study of social behavior and communal life of human being.
Biotechnology:
It deals with the use of living organisms, system or process to manufacturing and service industries.
Q.No 4
What are the bio-elements? What are various levels of biological organization?
Answer
BIO-ELEMENTS:
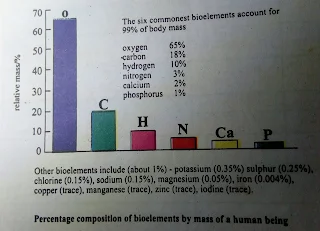
Sixteen out of the 92 naturally occurring elements are commonly used in forming the chemical compounds from which living organisms are made. These 16 elements and a few others, which occur in a particular organism, are called bio-elements.
In the human body only six bio-elements form about 99% of the total mass. Each element is made up of electron, proton and neutron.
MAN AND THE CONTROL OF DISEASE-CAUSING GERMS:
A large number of communicable diseases (from French Disaise mean lacking of ease ) are caused by germs or microbes. Although the list is very lengthy ,Of these, the main infecting agents are viruses and bacteria. These germs enter the human body through cuts in the skin, the air that is inhaled, the food and water that is taken in and through the bites of animals, especially insects. Germs cause diseases directly by attacking and destroying body cells and indirectly by producing poisonous substances called toxins. The virus of poliomyelitis destroys certain cells of the spinal cord while the diphtheria-causing bacterium (namely, Corynebacterium diphtheriae) produces a powerful toxin.
Natural defense Of Human body:
The human body's natural defence against such invaders are the white corpuscles in the blood which engulf bacteria, and certain cells in the lymphatic glands which produce antibodies. Antibodies can destroy the invading organism or make its toxin harmless. The type of antibody produced depends on the bacterium or virus which invades the body. Sometimes when a particular organism invades the body, enough anti-bodies are formed and retained in the body for a few months to a few years, in which case the person is said to have acquired an immunity against the disease.
Different ways to control diseases:
Most bacterial and viral diseases can be controlled by good health habits, sterilization of food and water, extermination of animals which carry disease germs, proper sanitary conditions, maintenance of bodily health and artificial immunity produced by vaccinations and inoculations.
Contribution of Edwards Jenner and Louis Pasteur:
Edward Jenner (1749-1823) and Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) have contributed greatly towards the use of artificial immunity as a means of controlling diseases. Certain disease-causing bacteria or viruses can be artificially altered so that their disease- causing abilities are reduced / minimize . When these are injected into the human body they cause the production of antibodies in the body but not the disease. The antibodies produced confer immunity against the disease for a period of time. This method of immunization is used for controlling diseases such as poliomyelitis, whooping cough and rabies. Sometimes, instead of inoculating a modified disease-causing agent, a modified toxin called a toxoid produced by the bacterium or virus is inoculated into the body. This also results in the formation of anti- Immunization against diphtheria and tetanus is brought about by this method since the serious effects of these diseases are due to the powerful toxins produced by the bacteria concerned. In most countries infants preschool and school children are immunized against smallpox, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough and poliomyelitis as a routine. Artificial immunity against diseases like cholera and typhoid fever lasts only for a short period (six months). There-fore, these inoculations are given when epidemics of these diseases occur.
Antibiotics:
Many diseases, caused by germs against which there are no vaccines, can be treated by the use of certain drugs. These drugs called antibiotics,
Examples:
penicillin, tetracyclins, streptomycin and aureomycin, inhibit the growth of disease causing germs. Antibiotics are produced by certain moulds, actinomycetes and bacteria.
Types of antibiotics:
There are two main categories of antibiotics.
1) Narrow spectrum antibiotics.
2) Wide spectrum antibiotics.




0 Comments